Exploring the World of Swiss Cheese: Types, Making Process, and More
Introduction
Swiss cheese, with its distinctive flavor and iconic holes, stands as a testament to the rich tradition of Swiss cheesemaking. Originating from the scenic landscapes of Switzerland, this cheese variety has transcended borders to become a global culinary favorite.
In this journey through the world of Swiss cheese, we delve into its various types, the meticulous art of Swiss cheesemaking, and the intriguing details behind those characteristic holes. From the nutty nuances of Emmental to the savory notes of Gruyère, each Swiss cheese variety offers a unique experience.
Join us as we explore the calories in Swiss cheese, unravel the mysteries of hole formation, and uncover the secrets of both traditional and modern cheesemaking techniques. Whether you’re a cheese connoisseur or simply curious about this dairy delight, our guide will take you on a flavorful expedition into the heart of Swiss cheese culture.
Swiss Cheeses
Switzerland, renowned for its picturesque landscapes, also boasts a rich legacy of cheese craftsmanship. Among the array of Swiss cheeses, three varieties stand out with distinct characteristics and flavors.
Emmental
- Characteristics: Emmental, the quintessential Swiss cheese, is identifiable by its large, round eyes or holes. Its pale yellow hue and firm texture contribute to its visual appeal.
- Flavor Profile: Known for its mild and nutty flavor, Emmental complements a variety of dishes. Its subtle sweetness intensifies as it ages.
- Culinary Uses: Emmental is a versatile cheese, celebrated in fondue and melted atop sandwiches. Its firmness allows for easy slicing and grating.
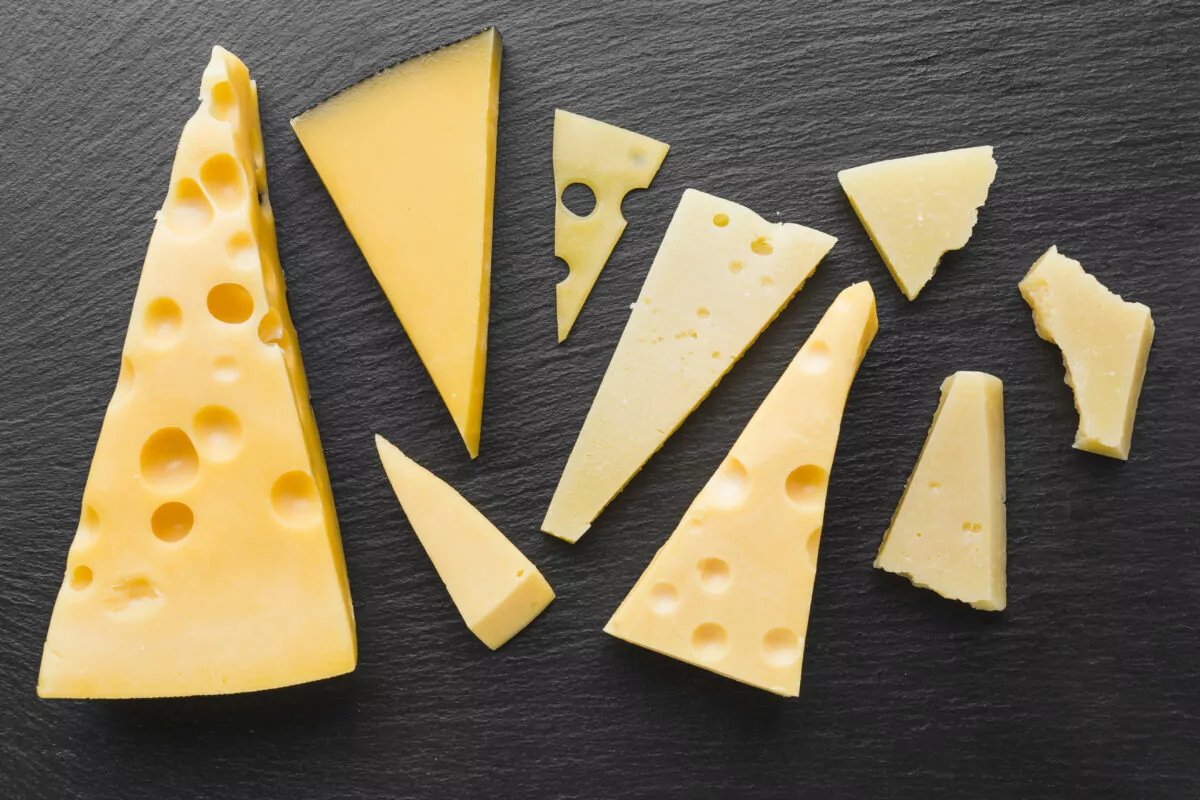

Gruyère
- Features: Gruyère, with a golden-yellow hue and a smooth texture, is recognized for its smaller, scattered holes.
- Taste: The flavor profile of Gruyère is robust, combining sweet and salty notes. Aging enhances its complexity and depth.
- Culinary Applications: Gruyère is a staple in French onion soup and a star in the classic Swiss dish, fondue. Its rich taste elevates both hot and cold dishes.
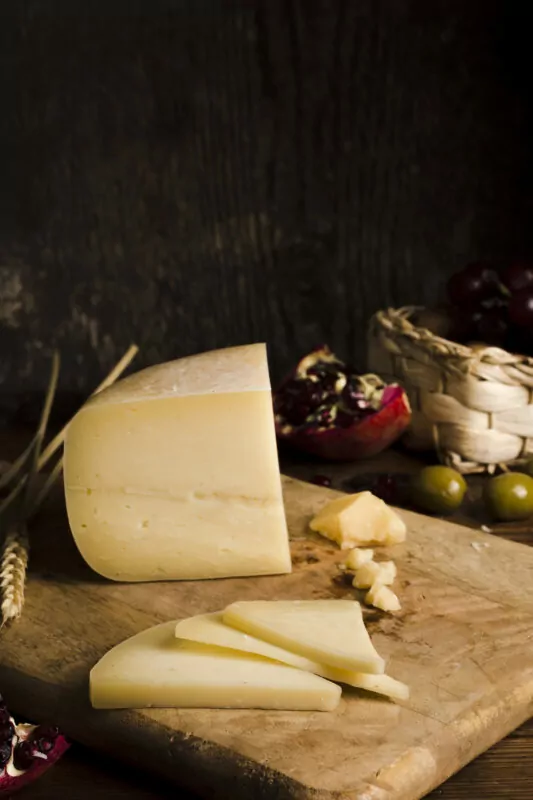

Appenzeller
- Attributes: Appenzeller, often identified by its brine-washed rind, exhibits a reddish-brown hue and a dense, creamy texture.
- Flavor Nuances: This cheese boasts a pungent and tangy flavor, thanks to the herbal brine used during its maturation. The result is a harmonious blend of savory and spicy notes.
- Usage in Dishes: Appenzeller is frequently grated over pasta or enjoyed on a cheese platter. Its bold flavor makes it a standout ingredient in various culinary creations.
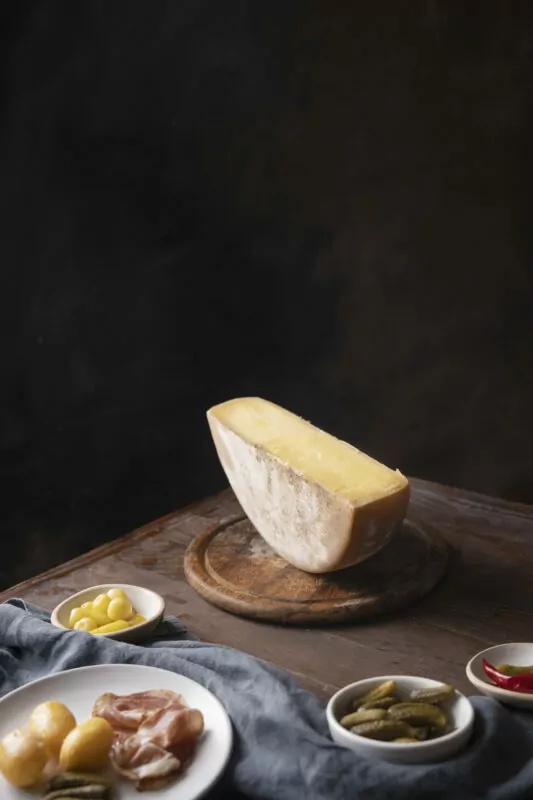

These traditional Swiss cheeses not only reflect the country’s dedication to quality but also provide a diverse range of tastes and textures for culinary enthusiasts to savor. As we explore the intricate world of Swiss cheesemaking, these varieties serve as ambassadors of a time-honored craft.
Swiss Cheesemaking
The art of Swiss cheesemaking is a meticulous process that has been honed over centuries, blending tradition with modern techniques. Understanding the journey from farm to table unveils the secrets behind the exceptional flavors and textures of Swiss cheeses.
Traditional Methods
- Milk Selection: The foundation of Swiss cheese lies in selecting high-quality milk. Local Swiss dairies often use raw cow’s milk, contributing to the cheese’s distinct character.
- The Role of Bacteria and Enzymes: Cheesemakers introduce specific bacteria and enzymes to initiate the fermentation and curdling process, crucial for flavor development and texture.
- Aging Process: After the initial curdling, the cheese undergoes a carefully monitored aging process. This step, which can last several months, allows the flavors to mature and intensify.
Modern Techniques
- Technological Advancements: While traditional methods remain the backbone of Swiss cheesemaking, technological advancements have streamlined certain processes. Temperature control and automation ensure consistency and quality.
- Quality Control: Rigorous quality control measures are implemented at every stage, from milk production to aging. This commitment to excellence guarantees that each wheel of Swiss cheese meets the highest standards.
- Sustainable Practices: Many Swiss cheesemakers are embracing sustainable practices, focusing on eco-friendly initiatives such as energy-efficient production and waste reduction.
Swiss cheesemaking is a harmonious blend of time-honored craftsmanship and contemporary innovation. The dedication to quality ingredients, coupled with the precision in each step, results in cheeses that captivate the palate. Whether following centuries-old traditions or incorporating modern technologies, Swiss cheesemakers continue to shape an industry that is both rooted in history and adaptable to the demands of the present.
Calories in Swiss Cheese
Swiss cheese, beyond its delectable taste and distinctive features, also holds nutritional value that makes it a wholesome addition to various dishes. Understanding the calorie content and nutritional profile allows enthusiasts to enjoy this cheese responsibly as part of a balanced diet.
Nutritional Profile
- Protein Content: Swiss cheese is a commendable source of high-quality protein, making it a favorable choice for those seeking to meet their protein needs.
- Fat Content: While Swiss cheese contains fat, it is often appreciated for its moderate fat content, contributing to a satisfying mouthfeel without excessive caloric intake.
- Other Essential Nutrients: Beyond proteins and fats, Swiss cheese offers essential nutrients such as calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin B12, supporting overall health.
Health Considerations
- Moderation: Like any cheese, moderation is key. While Swiss cheese is nutrient-dense, consuming it in moderation helps maintain a balanced diet.
- Incorporating Swiss Cheese into a Balanced Diet: Swiss cheese can be part of a healthy diet when paired with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Its versatility makes it suitable for various culinary creations.
- Dietary Restrictions: Individuals with specific dietary restrictions, such as lactose intolerance, can still enjoy Swiss cheese, as it generally contains lower lactose levels compared to other cheeses.
Understanding the caloric content of Swiss cheese empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices. Its nutritional richness, coupled with a mindful approach to consumption, allows people to savor the flavors of Swiss cheese while prioritizing their health and well-being.
Holes in Cheese
The distinctive feature that sets Swiss cheese apart from its counterparts is the presence of characteristic holes, also known as “eyes.” Unveiling the mystery behind these holes adds an intriguing layer to the already fascinating world of Swiss cheese.
Explanation of Holes in Swiss Cheese
- Formation During the Cheesemaking Process: The holes in Swiss cheese are a result of gas produced by bacteria during fermentation. As bacteria consume lactose in the milk, they release carbon dioxide, creating pockets within the cheese.
- The Role of Bacteria in Creating Holes: Propionibacterium, a group of bacteria introduced during the cheesemaking process, plays a crucial role. These bacteria produce carbon dioxide, which becomes trapped, forming the characteristic holes.
- Myths and Misconceptions: Contrary to popular belief, the holes do not indicate a lack of quality. In fact, they are a hallmark of well-made Swiss cheese. The size and distribution of the holes can vary, contributing to the unique visual appeal of each cheese wheel.
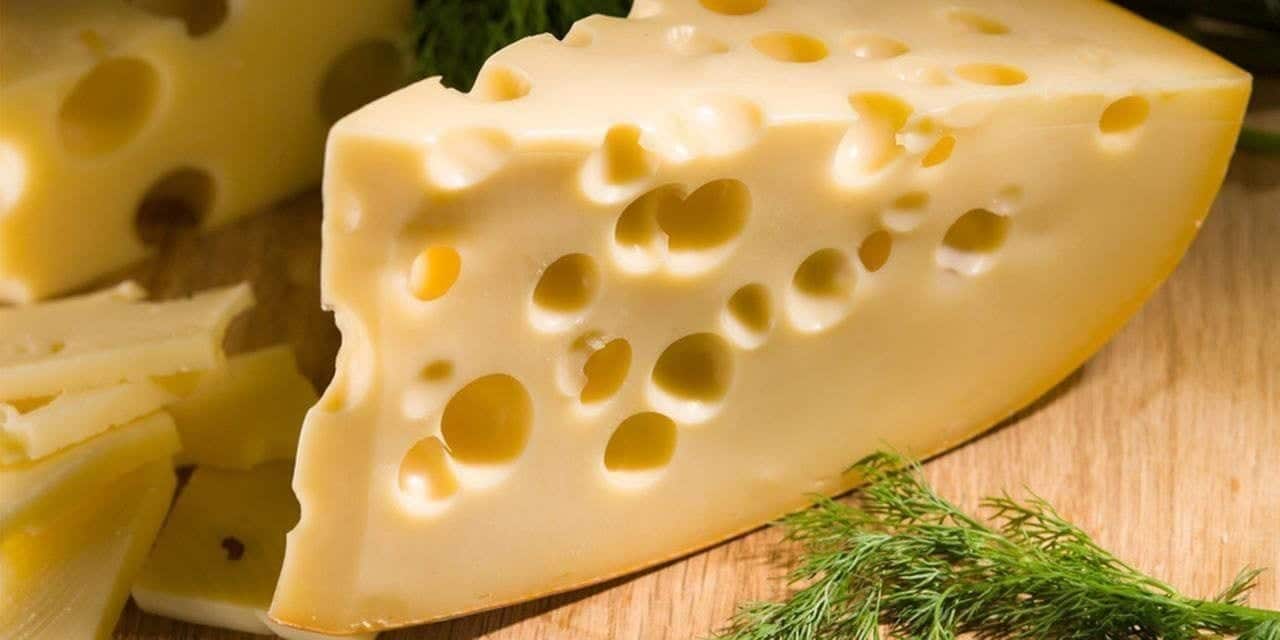

Understanding the science behind the holes in Swiss cheese enhances appreciation for the craftsmanship involved. These holes not only add visual intrigue but also contribute to the cheese’s texture and flavor, making each bite a delightful experience. As we continue our exploration of Swiss cheese, the presence of these holes becomes a fascinating element in the cheesemaking narrative.
How is Swiss Cheese Made
The production of Swiss cheese is a meticulous process that blends traditional methods with modern techniques. Understanding the step-by-step journey from raw milk to the finished product provides insight into the craftsmanship that goes into creating this beloved cheese.
Step-by-Step Process
- Milk Collection and Preparation: The process begins with the careful selection and collection of high-quality raw cow’s milk. The milk is then heated to the desired temperature, preparing it for the next stages.
- Curdling and Cutting: Specific bacteria cultures and enzymes are introduced to the milk to initiate the curdling process. Once the milk has coagulated, the curds are cut into small pieces, separating them from the whey.
- Pressing and Molding: The curds are pressed into molds to give the cheese its characteristic shape. During this phase, excess whey is expelled, and the curds are compacted to form a solid mass.
- Aging and Ripening: The cheese is transferred to the aging room, where it undergoes a carefully monitored maturation process. This period can last several months, during which the cheese develops its unique flavor, aroma, and texture.
Variations in Technique
- Traditional Techniques: Some cheesemakers adhere to time-honored practices, using raw milk and allowing for a longer, natural fermentation process. This approach imparts a distinct character to the cheese.
- Modern Innovations: Advances in technology have allowed for more controlled and efficient cheesemaking. Temperature and humidity are closely monitored, ensuring consistency and quality.
Understanding how Swiss cheese is made unveils the artistry and science behind this iconic dairy product. From the careful selection of raw milk to the patient aging process, each step contributes to the development of the unique flavors and textures that define Swiss cheese. Whether produced with traditional methods or incorporating modern innovations, the commitment to quality remains at the heart of Swiss cheesemaking.
American Swiss Cheese
While traditional Swiss cheeses have earned global acclaim, American Swiss cheese has carved its own niche in the culinary world. Originating from European roots, American Swiss cheese has undergone unique adaptations to suit diverse palates and preferences.
Origin and Development
- European Influence: The roots of American Swiss cheese can be traced back to Swiss immigrants who brought their cheesemaking traditions to the United States.
- Adaptations for American Tastes: Over time, American cheesemakers introduced variations to the traditional Swiss recipes to cater to the evolving taste preferences of the American consumer.
Key Differences from Traditional Swiss Cheeses
- Texture and Melting Properties: American Swiss cheese is often known for its smooth, creamy texture and excellent melting properties. This makes it a popular choice for sandwiches and burgers.
- Mild Flavor Profile: Compared to its Swiss counterparts, American Swiss cheese typically has a milder flavor. This makes it versatile and appealing to a broader audience.
Culinary Uses and Popularity
- Sandwich Staple: American Swiss cheese has become a staple in deli sandwiches, especially in the classic Reuben sandwich. Its mild flavor complements a variety of meats and condiments.
- Melting Properties: The cheese’s excellent melting capabilities make it a favorite for grilled cheese sandwiches, burgers, and other melted cheese applications.
- Snacking and Pairing: American Swiss cheese is also enjoyed on cheese platters and paired with fruits, crackers, and nuts.
American Swiss cheese, while inspired by its European roots, has evolved into a distinct cheese variety appreciated for its smooth texture, mild flavor, and culinary versatility. Whether melted on a hot sandwich or enjoyed on its own, American Swiss cheese continues to hold a special place in the hearts and palates of cheese enthusiasts across the United States.
Swiss Cheese Variety
Swiss cheese, a testament to the rich cheesemaking heritage of Switzerland, offers a diverse range of varieties that cater to a spectrum of tastes and preferences. From regional nuances to artisanal creations, the Swiss cheese variety is a vibrant tapestry of flavors and textures.
Regional Variations
- Swiss Cheese in Different Cantons: Each Swiss canton boasts its own unique cheese traditions, contributing to the diversity of Swiss cheese. For example, the alpine regions may produce cheeses with distinct herbal notes.
- Unique Flavors and Characteristics: From the nutty Emmental of the Bernese Oberland to the aromatic Appenzeller from the eastern regions, the geography and terroir influence the flavors and characteristics of Swiss cheeses.
Artisanal and Specialty Swiss Cheeses
- Craftsmanship of Local Cheesemakers: Artisanal Swiss cheeses are crafted by local cheesemakers who often employ traditional methods and source milk from specific localities, resulting in unique and nuanced flavors.
- Innovative Flavors and Blends: Some Swiss cheesemakers are experimenting with innovative flavors and blends, incorporating ingredients like herbs, spices, or even wine, to create contemporary twists on traditional favorites.
The Swiss cheese variety goes beyond the well-known Emmental and Gruyère, offering a delightful exploration of tastes and textures. Whether you’re savoring a cheese with roots in a specific canton or indulging in an artisanal creation, the Swiss cheese variety is an invitation to experience the breadth and depth of a rich cheesemaking tradition that continues to evolve and captivate the palate.
Swiss Cheese Types
Swiss cheese, celebrated for its diverse and nuanced flavors, is available in various types that cater to different preferences and culinary applications. From mild to aged, and traditional to innovative blends, the types of Swiss cheese offer a delightful spectrum for cheese enthusiasts to explore.
Diverse Options for Various Preferences
- Mild vs. Aged Swiss Cheese: Swiss cheese comes in both mild and aged varieties. Mild Swiss cheese is characterized by its smooth texture and subtle nutty flavor, while aged Swiss cheese develops a richer and more pronounced taste during the maturation process.
- Flavored Swiss Cheeses: Some Swiss cheeses are infused with additional flavors, such as herbs, spices, or even fruits. These flavored varieties add a unique twist to the traditional Swiss cheese profile.
- Swiss Cheese Blends: Cheesemakers often experiment with blending Swiss cheese with other cheese varieties, creating new and exciting combinations that offer a fusion of flavors.
Exploring Flavor Profiles
- Nutty Nuances: Swiss cheeses like Emmental are known for their distinct nutty nuances, contributing to their versatile use in various culinary dishes.
- Savory Notes: Gruyère, with its savory flavor profile, is a popular choice for both melting and snacking.
- Bold and Pungent Flavors: Cheeses like Appenzeller, with their bold and pungent flavors, add a robust dimension to dishes.
Culinary Applications
- Cheese Boards: Swiss cheese varieties make excellent additions to cheese boards, offering a range of textures and flavors for pairing with fruits, nuts, and crackers.
- Cooking and Melting: The melting properties of Swiss cheese, especially varieties like Gruyère, make them ideal for fondue, gratins, and other melted cheese dishes.
- Snacking and Sandwiches: Mild Swiss cheeses, including American Swiss, are popular choices for snacking and sandwiches, providing a creamy and versatile option.
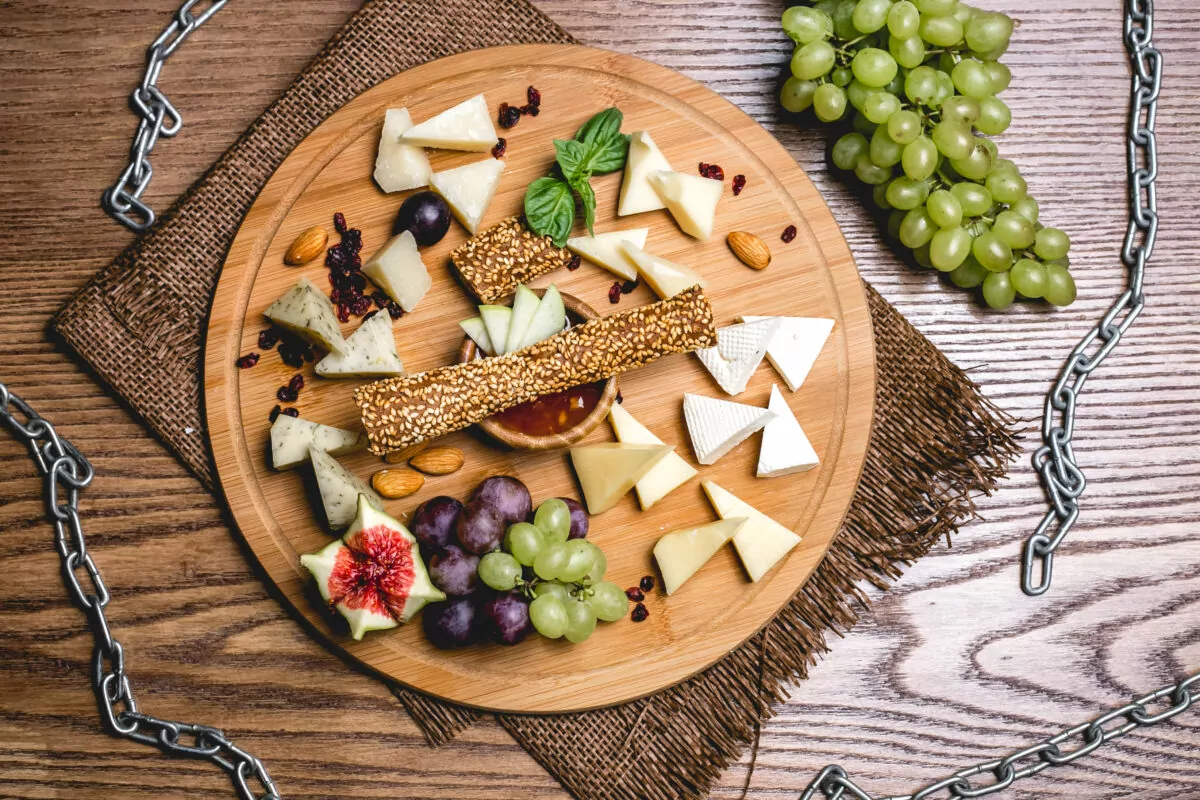

As you embark on a journey through Swiss cheese types, the vast array of options invites you to savor the nuances and explore the creative expressions that arise from the rich tradition of Swiss cheesemaking. Whether enjoyed on its own or as a key ingredient in a culinary masterpiece, Swiss cheese types continue to captivate taste buds around the world.
Conclusion
We invite you to savor the richness of its varieties, appreciate the expertise of its cheesemakers, and explore the endless possibilities it offers in the world of gastronomy. Whether you’re a cheese enthusiast or a culinary adventurer, Swiss cheese stands as a testament to the timeless appeal of artisanal craftsmanship and the enduring love for exceptional flavors. Cheers to the delectable world of Swiss cheese, where every bite is a celebration of tradition, innovation, and the sheer joy of indulging in one of the finest cheeses the world has to offer.


 Littauerboden 1 CH-6014, Luzern Switzerland
Littauerboden 1 CH-6014, Luzern Switzerland info@swissmade.direct
info@swissmade.direct

